Osteoarthritis / Arthritis is a degenerative disease where cartilage in the joints of the body get worn down eventually leaving the bone exposed causing endless amount of pain who anyone who suffers with it. Normal or “healthy” cartilage acts as support in the joint, which allows the bone to run smoothly, when damaged it becomes rough causing discomfort for many people.
Anatomy
The hip is a ball and socket joint and is one of the largest joints in the body. The acetabulum is a part of the pelvis bone which allows the head of the femur to move freely in the socket.
Articular cartilage is a slippery substance which covers the joint, this helps protect and allows free unpainful movement in the ball and socket. Within the hip synovium can be found, this also helps lubricate the joint to allow the hip to function properly.
A person who is suffering with arthritis of the hip will have cartilage that is worn down and will not be producing enough fluid to allow the free movement. This will lead to the bone rubbing against another bone creating discomfort and pain for an individual.
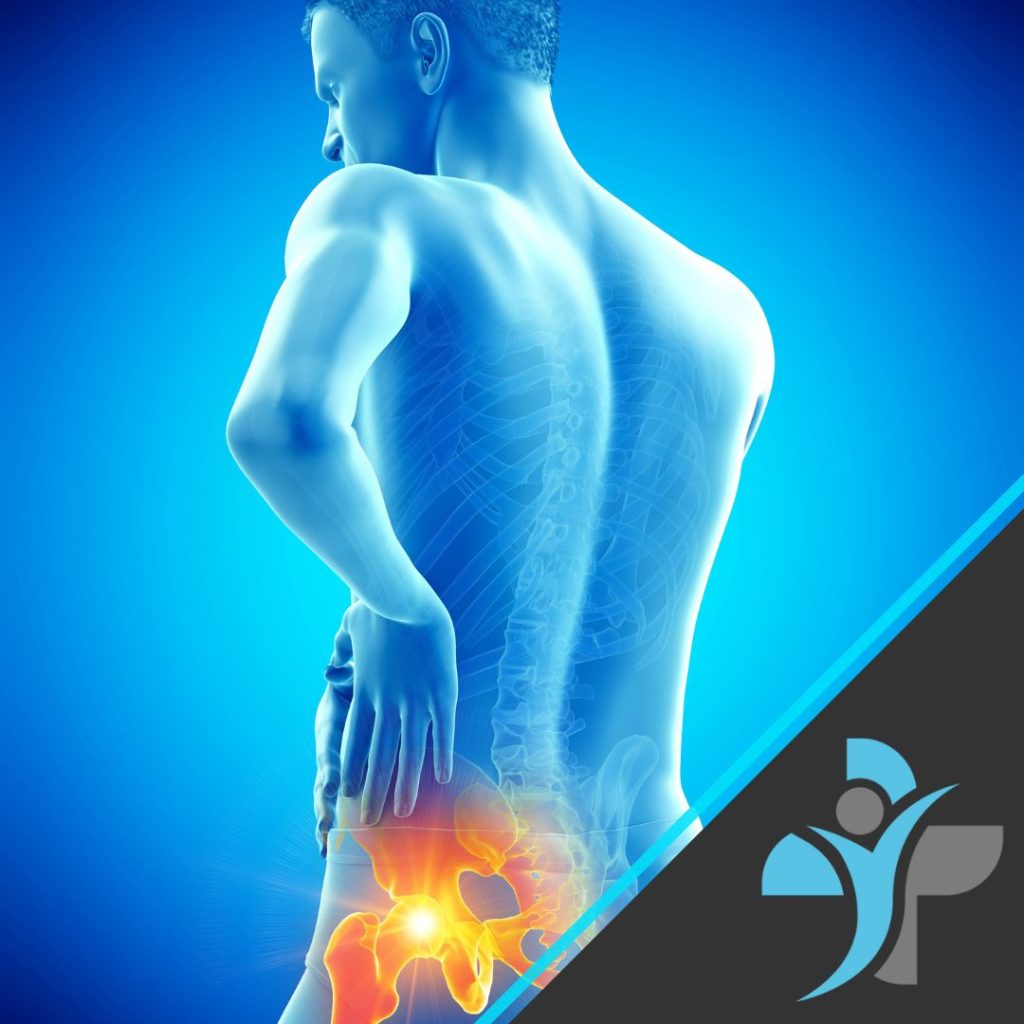
Symptoms
- Stiffness around the hip joint
- Flare ups when walking, running or performing exercise
- Pain when resting
- Daily discomfort and ongoing pain in the joint
- Stiffness in the groin, thigh and glutes when walking
- Swelling around the hip
- Grinding sensation in the joint when moving
Causes
- Arthritis is more common as you get older
- Family history is a common factor of hip arthritis
- Individuals who are more overweight often show on going signs of arthritis
- An injury to the hip and overuse may lead to the long-term effects of arthritis
Diagnosis
A full physical examination will be carried out by a doctor to determine the severity of your condition.
The doctor will carry out special tests specific for the hip to see what movements create the most pain and discomfort. The professional will need to know information such as when the pain first started to occur, how if effects your sleep and how it affects your day-to-day life and activities.
Special tests that are used for the diagnosis of hip arthritis are Trendelenburg test, supine (leg length test) and gait test.
Treatment
Non- surgical treatment that may be effective to help reduce the pain from arthritis are as follows:
- One of the most successful forms of treatment is to have a deep tissue or sports massage. The reason for this is to lengthen the muscles, relax the muscles around the Hip such as the Glutes etc in order to alleviate some of the pressure in the joint.
- Ensuring you rest enough when the hip joint is in any pain to reduce irritating the arthritis
- Preform non-weight baring exercises such as swimming or a gentle cycle to reduce any added pressure onto the hip, this allows the hip to still have good range of motion and keeps the joint functioning
- Make sure you are getting enough sleep and resting the hip
- Try eating a healthier balanced diet, this will help with weight loss and reduce the amount of stress placed onto the joints
- Use over the counter treatment such as deep freeze which may help reduce pain and swelling around the joint
If the pain is ongoing, it is worth speaking to your doctor who may suggest surgery as a last resort. This would mean you would undergo a hip replacement, where you would then follow an 8–12-week rehabilitation programme.
Exercises
These exercises should be performed in sets and reps, it is best to speak to a doctor or physiotherapist to find out the recommended amount suitable for you:
1. Seated Hip Flexion
- Purpose: Improve hip flexor strength and maintain mobility in the hip joint, which can help alleviate stiffness and pain from arthritis.
- How to Perform:
- Sit on a chair with your feet flat on the floor.
- Lift one knee toward your chest while keeping your back straight.
- Lower your leg back down slowly and repeat with the other leg.
2. Sit to Stand
- Purpose: Strengthen the muscles around the hip joint, particularly the quadriceps and glutes, to improve stability and reduce pain from hip arthritis.
- How to Perform:
- Sit on a chair with your feet hip-width apart and your hands on your thighs or crossed in front of you.
- Lean slightly forward and push through your heels to stand up, using your leg muscles rather than your arms.
- Slowly lower yourself back down to the chair and repeat.
3. Kneeling Hip Flexor Stretch
- Purpose: Stretch the hip flexors, which can become tight and contribute to pain and reduced mobility in people with hip arthritis.
- How to Perform:
- Kneel on one knee with the other foot in front of you, forming a 90-degree angle at both knees.
- Gently push your hips forward, stretching the front of your hip on the kneeling side.
- Hold the stretch for 20-30 seconds, then switch legs and repeat.
4. Hip Abduction in Supine Position
- Purpose: Strengthen the hip abductors, particularly the gluteus medius, which helps support and stabilise the hip joint.
- How to Perform:
- Lie on your back with your legs straight and slightly apart.
- Keeping your leg straight, slowly slide one leg out to the side as far as comfortable, then return it to the starting position.
- Repeat with the other leg.
5. Hip Extension
- Purpose: Strengthen the glutes and hamstrings, improving hip stability and reducing pain from arthritis.
- How to Perform:
- Stand with your feet hip-width apart and hold onto a sturdy surface for balance.
- Keeping your leg straight, slowly lift one leg backward, squeezing your glutes.
- Lower the leg back down slowly and repeat with the other leg.
6. Glute Bridges
- Purpose: Strengthen the glutes and lower back muscles, providing better support for the hip joint and reducing arthritis symptoms.
- How to Perform:
- Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor, hip-width apart.
- Lift your hips toward the ceiling, squeezing your glutes and keeping your body in a straight line from shoulders to knees.
- Hold for a few seconds at the top, then slowly lower your hips back down.
7. Body Weight Squat
-
- Purpose: Strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, which helps support and stabilise the hip joint.
- How to Perform:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Slowly lower your body by bending your knees and hips, keeping your back straight and your weight on your heels.
- Lower as far as comfortable, then push through your heels to stand back up
Prevention
Prevention of hip arthritis involves making lifestyle changes and taking steps to reduce your risk of developing the condition. Here are some tips for preventing hip arthritis:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese puts additional stress on your hip joint, increasing your risk of developing arthritis.
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve your joint health, flexibility, and strength.
- Avoid overuse injuries: Repeated stress on the hip joint can lead to arthritis over time.
- Use proper technique: When performing physical activities or exercises, use proper technique
- Wear appropriate footwear
Avoid sitting for long periods: Sitting for extended periods can increase the pressure on your hips.
Manage other health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, can increase your risk of developing hip arthritis. Work with your healthcare provider to manage these conditions and reduce your risk.
By making these lifestyle changes and taking steps to reduce your risk of developing hip arthritis, you can help protect your hip joints and maintain good overall health.
If you are suffering with Hip Arthritis and would like to Make a booking or speak with one of our Phsyiotherapists or Sports Therapists then please contact us today.

